Geographic Indications and International Trade (GIANT)
TED Case Studies
BASMATI
CASE MNEMONIC: Basmati
CASE NAME: India-US Basmati Rice Dispute

<
I. Identification
1. The Issue
In late 1997, an American company RiceTec Inc, was granted a patent by the US patent office to call the aromatic rice grown outside India 'Basmati'. RiceTec Inc, had been trying to enter the international Basmati market with brands like 'Kasmati' and 'Texmati' described as Basmati-type rice with minimal success. However, with the Basmati patent rights, RiceTec will now be able to not only call its aromatic rice Basmati within the US, but also label it Basmati for its exports. This has grave repercussions for India and Pakistan because not only will India lose out on the 45,000 tonne US import market, which forms 10 percent of the total Basmati exports, but also its position in crucial markets like the European Union, the United Kingdom, Middle East and West Asia. In addition, the patent on Basmati is believed to be a violation of the fundamental fact that the long grain aromatic rice grown only in Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh is called Basmati. According to sources from the Indian Newspaper, Economic Times, "Patenting Basmati in the US is like snatching away our history and culture."(1)
2. Description

Basmati rice means the "queen of fragrance or the perfumed
one." This type of rice has been grown in the foothills of the Himalayas for thousands of
years. Its perfumy, nut-like flavor and aroma can be attributed to the fact that the grain is
aged to decrease its moisture content. Basmati, a long-grained rice with a fine texture is the
costliest rice in the world and has been favored by emperors and praised by poets for hundreds of
years. According to the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority
(APEDA), India is the second largest producer of rice after China, and grows over a tenth of the
world's wheat. In 1993, Basmati rice attracted the highest premium because it is a very-long
grained rice, with an aroma of its own which enhances the flavors its mixed with.
The Rice Patent
RiceTec Inc, was issued the Patent number
5663484 on Basmati rice lines and grains on September 2, 1997.
In abstract, "the invention relates to novel rice lines and to plants and grains of these lines. The invention also relates to a novel means for determining the cooking and starch properties of rice grains and its use in identifying desirable rice lines. Specifically, one aspect of the invention relates to novel rice lines whose plants are semi-dwarf in stature, substantially photoperiod insensitive and high yielding, and produce rice grains having characteristics similar or superior to those of good quality Basmati rice. Another aspect of the invention relates to novel rice lines produced from novel rice lines. The invention provides a method for breeding these novel lines. A third aspect...relates to the finding that the starch index (SI) of a rice grain can predict the grain's cooking and starch properties, to a method based thereon for identifying grains that can be cooked to the firmness of traditional Basmati rice preparations, and to the use of this method in selecting desirable segregants in rice breeding programs." (2)
Importance of Rice on Indian and Pakistan Economy
Rice is an important aspect of life in the Southeast and other parts of Asia. For centuries, it has been the cornerstone of their food and culture. During this period, farming communities throughout the region developed, nurtured, and conserved over a hundred thousand distinct varieties of rice to suit different tastes and needs. It is for this reason that patenting of Basmati by RiceTec Inc. is perceived as not only intellectual property and cultural theft, but it also directly threatens farm communities in Southeast Asia. According to Dr Vandana Shiva, director of a Delhi-based research foundation which monitors issues involving patents and biopiracy, the main aim for obtaining the patent by RiceTec Inc. is to fool the consumers in believing there is no difference between spurious Basmati and real Basmati. Moreover, she claims the "theft involved in the Basmati patent is, therefore, threefold: a theft of collective intellectual and biodiversity heritage on Indian farmers, a theft from Indian traders and exporters whose markets are being stolen by RiceTec Inc., and finally a deception of consumers since RiceTec is using a stolen name Basmati for rice which are derived from Indian rice but not grown in India, and hence are not the same quality."(3) In fact, Basmati rice has been one of the fastest growing export
items from India in recent years. In the year to March 1997, India exported more than half a
million tonnes of Basmati to the Gulf, Saudi Arabia, Europe and the United States, a small part
of its total rice exports, but high in value. More substantively, Indian farmers export $250
million in Basmati every year and U.S. is a target market. (4) RiceTec Inc. had attempted to sell
its long-grain rice in Europe under such brand names as 'Texmati' and 'Kasmati' but not as
Basmati. However, if the patent is not revoked, RiceTec Inc., can now sell its rice under the
brand name Basmati which will definitely cut into India's and Pakistan's global market share,
especially as the rice grown in the US could be sold cheaper than the Indian and Pakistani
varieties.
The Government of India's response to the
Patent
In an official release, the government of India reacted immediately
after learning of the Basmati patent issued to RiceTec Inc., stating that it would approach the
US patent office and urge them to re-examine the patent to a United States firm to grow and sell
rice under the Basmati brand name in order to protect India's interests, particularly those of
growers and exporters. Furthermore, a high level inter-ministerial group comprising of
representatives of the ministries and departments of commerce, industry, external affairs,
Council for scientific and industrial research (CSIR), Agriculture, Bio-technology, All India
Rice Exporters Association (AIREA), APEDA, and Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
were mobilized to begin an in-depth examination of the case. The contents and implications of the
patent are currently being analyzed in consultation with patent attorneys and agricultural
scientists. The government of India is particularly concerned about the patenting of Basmati
because of an earlier case where the US granted a patent to two Indian-born scientists on the use
of Turmeric as a wound healing agent. This case worked in favor of India because the patent was
subsequently revoked after scientists of (CSIR) successfully challenged the patenting on the
ground that the healing properties of Turmeric had been 'common knowledge' in India for
centuries. There is a clause in US patent laws that will accept any information already available
in published or written form anywhere in the world as 'common knowledge'. As a result, India was
able to furnish published evidence to support their case that the healing characteristics of
Turmeric is not a new invention and as such cannot be patented.
In the presence of widespread uprising among farmers and exporters, the
nation of India as a whole feel confident of being able to successfully challenge the Basmati
patent by RiceTec Inc. According to the Economic Times of India, the law firm of Sagar and Suri
who won the Turmeric patent case and presently representing the government against RiceTec Inc.
in existing cases, said; "RiceTec has got a patent for three things: growing rice plants with
certain characteristics identical to Basmati, the grain produced by such plants, and the method
of selecting the rice plant based on a starch index (SI) test devised by RiceTec Inc." The
lawyers plan to challenge this patent on the basis that the above mentioned plant varieties and
grains already exist and thus cannot be patented. In addition, they encountered some information
from the US National Agricultural Statistics Service in its latest Rice Year book 1997, released
in January 1998, which states that almost 75 percent of US rice imports are the Jasmine rice from
Thailand and most of the remainder are from India and Pakistan,"varieties that cannot be grown in
the US" This piece of information is rather interesting and can be used as a weapon against the
RiceTec Basmati patent. (5)
Legal procedures of Obtaining a Patent in
the US and India
The law firm representing India in the dispute, Sagar and
Suri, criticized the procedures for granting patents in the US claiming it is diametrically
opposite to the one followed in India and Europe. According to them, India first examines a
patent application, then widely publishes it for third parties to challenge, and only then grants
the patent. However, the US keeps the patent application a closely guarded secret and grants it
without allowing other parties to challenge it. After the patent has been granted, third parties
are then allowed to petition against the patent as India is currently doing in the Basmati
case. This criticism clearly illustrates the shortfalls in the patent process in the US that
ultimately needs to be revised to prevent future cases like this from occurring. (6)
TRIPS and World Trade Organization
Indians feel that the US
government's decision to grant a patent for the prized Basmati rice violates the International
Treaty on Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS). The president of the Associated
Chambers of Commerce (ASSOCHAM) said Basmati rice is traditionally grown in India and Pakistan
and granting patent to it violated the Geographical Indications act under the TRIPS. The TRIPS
clause defines Geographical indication as "a good originating in the territory of a member, or
a region or locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation, or other
characteristic of the good is essentially attributable to its geographical origin." As a
result, it is safe to say Basmati rice is as exclusively associated with India and Pakistan as
Champagne is to France and Scotch Whiskey is to Scotland. Indians argue that just as the US
cannot label their wine as champagne, they should not be able to label their rice Basmati. If the
patent is not revoked in the US because unlike the Turmeric case, rice growers lack documentation
of their traditional skills and knowledge, then India as have been urged by many activist in the
field should take the case to the WTO for an authoritative ruling based on the violation of
TRIPS. (7)
In the wake of the problems with patents that India has experienced in
recent years, they have now realized the importance of enacting laws for conserving biodiversity
and controlling piracy as well as intellectual protection legislation that conform to
international laws. There is a widespread belief that RiceTec Inc., took out a patent on Basmati
only because of weak, non-existent Indian laws and the government's philosophical attitude that
natural products should not be patented. According to some Indian Experts in the field of genetic
wealth, India needs to formulate a long-term strategy to protect its bio-resources from future
bio-piracy and or theft. (8)
India and Pakistan who are joining hands to tackle the
crisis have a strong case against RiceTec Inc. British traders are also supporting India and
Pakistan. According to Howard Jones, marketing controller of the UK's privately owned distributor
Tilda Ltd, "True Basmati can only be grown in India or Pakisatn. We will support them in any way
if its necessary." (9)
The Middle East is also showing support by only labeling Indian or
Pakistani rice as Basmati. The case is still unfolding and it will be interesting to find out
what happens in the end once the government and government agencies have gathered the necessary
data and information to support their case and to prevent their cultural heritage from being
taken away from them.
3. Related Cases
4. Draft Author: Jolayemi Adewumi; June (1998)
 II.
Legal Clusters
II.
Legal Clusters
5. Discourse and Status: Disagreement and Allegation
6. Forum and Scope: Bilateral
7. Decision Breadth: Three; India, Pakistan and US
8. Legal Standing: Treaty
 III. Geographic Clusters
III. Geographic Clusters
9. Geographic Locations
a. Geographic Domain: ASIA
b. Geographic Site: South Asia
c. Geographic Impact: India and Pakistan
10. Sub-National Factors: No
11. Type of Habitat: Temperate
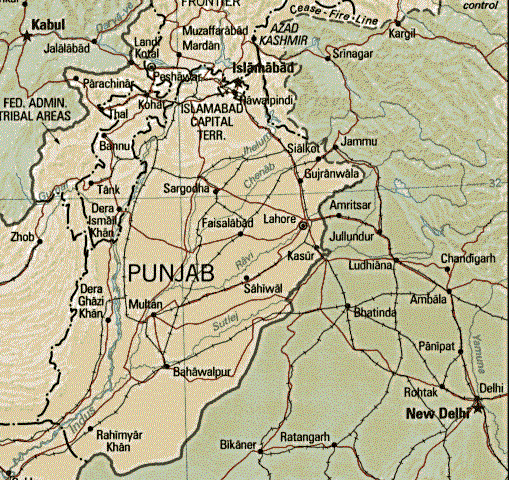
Every crop species has its own ecological requirements. Rice is grown under a damp warm climate. A temperature range of 20ºC to 37.7º C (68º F to 100º F) is required for the optimum growth of rice. Rice being a semi-aquatic crop, grows best under submerged, waterlogged conditions. Rice is able to tolerate a wide range of soil reactions, but has a preference of acidic soils. Click here to learn more about the Climate and Landscape of Punjab where Basmati rice is grown. IV. Trade
Clusters
IV. Trade
Clusters
12. Type of Measure: Intellectual Property Rights
The type of measure being utilized is accusing the RiceTec Inc and the US of violating the Geographical indication act of the TRIPS agreement in the WTO. But first, India and Pakistan would file a petition to the US patent office to re-examine the patent on Basmati claiming Basmati has been grown in their regions for thousands of years and is common knowledge in India and thus cannot be patented.13. Direct v. Indirect Impacts: Direct
14. Relation of Trade Measure to Environmental Impact: None
a. Directly Related to Product: Yes Basmati rice
b. Indirectly Related to Product: No
c. Not Related to Product: No
d. Related to Process: Yes Bio-diversity loss
15. Trade Product Identification: Basmati rice
According to a major Indian exporter of rice,GN overseas, "Rice is the staple food of more than 70% of the world's population. The rice belt is distributed geographically over a wide range of conditions between latitudes 45 ºN to 40 ºS. However, 90% of total area under rice is situated in the wet tropical South and South East Asia. Among the rice growing countries, India has the largest area under rice in the world, accounting for about 31% of the total area under rice cultivation. India is producing about 80 million tonnes of rice annually."(10)
Method for Identification of
Rice
| Sl No. | Characteristics | Basmati (in-mm) | Basmati (Paraboiled) | Parmal (PR-106) |
Terricot |
| 1 | Average Length of uncooked rice | 7.3 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 7.6 |
| 2 | Average breadth of uncooked rice | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 1.9 |
| 3 | Average L/B ratio of uncooked rice | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.3 | 4.0 |
| 4 | Average length of cooked rice | 8.9 | 8.9 | 5.6 | 8.0 |
| 5 | Average breadth of cooked rice | 2.2 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 3.0 |
General
Characteristics and Specifications of Rice
| Type of Rice | Grade | Purity Level | Grain | Broken | Moisture | Foreign Matter | Red Streak & Wary Grains |
| Basmati | Superior | 90% | 7mm | less than | 14% | Nil | less than 1% |
| & above | (Avg.) | 1% | |||||
| A | 85% | 6-7mm | less than 1% | 14% | Nil | less than 1% | |
| B | 75% | 5-7mm | less than 1% | 14% | Nil | less than 1% | |
| Non Basmati | Terricot | 100% | 14% | Nil | less than 1% | ||
| PR 106 | 100% | 14% | Nil | less than 1% | |||
| IR8 | 100% | 14% | Nil | less than 1% |
16. Economic Data
India exports about 400,000 - 500,000 metric tons of Basmati annually. In 1996-97, India exported approximately 523,000 tonnes of Basmati to Europe.17. Impact of Trade Restriction: High
18. Industry Sector: Food
19. Exporters and Importers: India and many; US and many.
 V. Environment
Clusters
V. Environment
Clusters
20. Environmental Problem Type: Habitat Loss
21. Name, Type, and Diversity of Species: Many
22. Resource Impact and Effect: Low and Regulatory
23. Urgency and Lifetime: Low and 1 year
24. Substitutes: Like products
 VI. Other Factors
VI. Other Factors
25. Culture: Yes
 As mentioned earlier, Basmati is a slender, aromatic long-grain
rice with a nutty taste delicate texture that grows best in the valleys of Punjab in the
Himalayan mountains . For countless generations, Punjabi (refer to the map above for its
location) farmers in the region nurtured the fragrant seeds while improving the yield. Basmati
originated in Punjab which spans areas of both India and Pakistan. This explains why its only
grown in those two countries. Punjab is one of the smallest states in India. However, its geology
that is, its deep and fertile soils as well as its exceptional climate has a far reaching impact
on India's economy.
As mentioned earlier, Basmati is a slender, aromatic long-grain
rice with a nutty taste delicate texture that grows best in the valleys of Punjab in the
Himalayan mountains . For countless generations, Punjabi (refer to the map above for its
location) farmers in the region nurtured the fragrant seeds while improving the yield. Basmati
originated in Punjab which spans areas of both India and Pakistan. This explains why its only
grown in those two countries. Punjab is one of the smallest states in India. However, its geology
that is, its deep and fertile soils as well as its exceptional climate has a far reaching impact
on India's economy. Basmati is viewed as a cultural heritage. Below are pictures of
different varieties of Basmati rice produced by an indian company Khushi Ram Behari Lal Ltd. This company, in their profile, claim
that four generations of the family have been in the rice business since 1889. This further
supports the argument that Basmati has existed in India and Pakistan for centuries and as such
cannot be patented by the US.
Three Varieties of Basmati
Rice
 Golden Parboiled Basmati |  Raw Basmati |  Silky Raw Basmati | ||||||||||||
26. Trans-Boundary Issues: No
27. Rights: Yes
28. Relevant Literature

- Economic Times of India
- India Server
- Indian Exporters Online
- Science and Patent Information
- India says may appeal U.S. Basmati rice Patent
- Hindu Daily news
- Indolink
- Business Standard Economy
- SciWeb
- Rediff on the Net
Endnotes
1. http://www.economictimes.com/today/12home1.htm
2. http://www.sciweb.com/home/eddyjake/patents/patents_800_10_2_97.html< br>
3. http://www.rediff.com/business/1998/mar/12rice.htm
4. http://data.free.de/gentec/gentech/1998/Mar-May/msg00073.htm
5. http://www.economictimes.com/today/12econ11.htm
6. Ibid.
7. http://www.indiaserver.com/bline/stories/04130032.htm
8. http://www.rediff.com/business/1998/mar/23rice.htm
9. http://www.business-standard.com/98apr07/economy4.htm
10. http://www.nyeq.com/GN overseas/grice.htm
