
| ICE Case Studies
|
|
I.
Case Background |

Lake Chiuta sits on the border between Mozambique and land-locked Malawi. The lake has a number of commercial fish that are taken by people on both sides of the river. The size of lake is varied and depends on the season. As demand has grown, the fish are becoming scarce in some seasons. This has led to violence. Armed fishermen from Mozambique have injured at least three Malawian fishermen.
Lake Chiuta is close to but not in the African Rift Valley that connects to the much larger LakeMalawi to the north. It is only 10-15 feet deep and probably comparable to the Parana in South America. It's size can range 10-50 to 130 square miles, but this is highly seasonally dependent. It is sometimes fed by the Lugenda River, but again this is a seasonal disposition.
Environmental conflict in this instance has a very local focus but with a multitude of dimensions. It is the combination of a number of inter-twined environmental factors: regular weather cycles, climate change, species loss, rising populations, and increasing hunger, to name only a few. A war over fish seems represent acts of desperation.
Malawi History
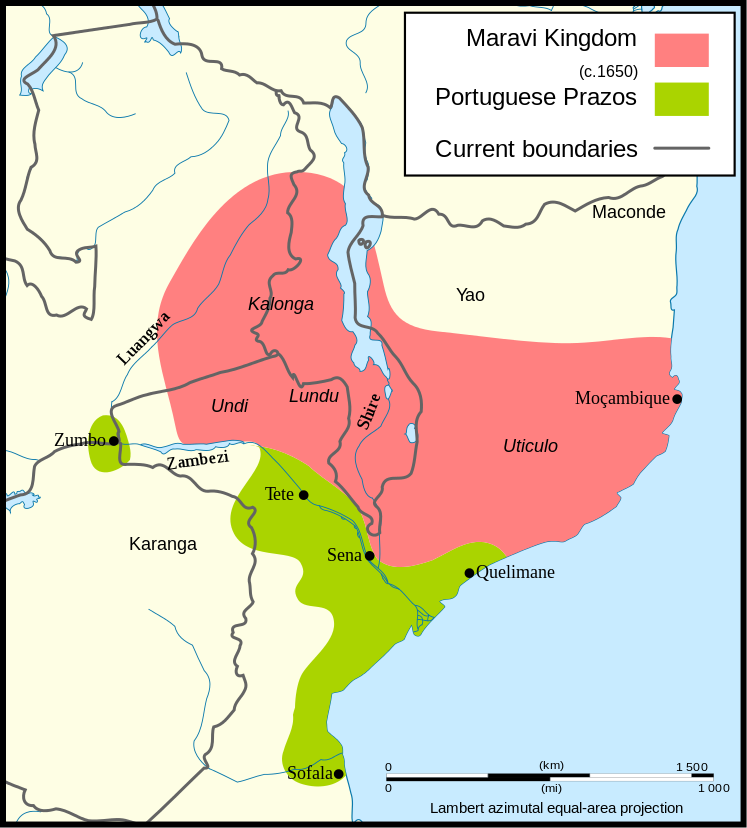
The Marawi Empire was incorporated into the British Empire and the country did not achieve indepence until 1964. It was ruled by one man until 1992. The Portugese were the first Europeans to contact the Maravi Empire in the 16th century.
 By Africa_map_blank.svg: Eric Gaba (Sting - fr:Sting)derivative work: moyogo (talk) - Africa_map_blank.svg, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
By Africa_map_blank.svg: Eric Gaba (Sting - fr:Sting)derivative work: moyogo (talk) - Africa_map_blank.svg, CC BY-SA 3.0, Link
Portugal acquired slaves from Malawi that were sent to Mozambique or Brazil. The empire declined with the migration of two groups. First, there were the Angoni who were a tribe fleeing from the Zulu's and their warrior-king Shaka Zulu. (See Zulu Case). Second, there were the Ayao, who had just migrated from northern Mozambique to to both famine and warfare.
Continent: Africa
Region: Southern Africa
Country: Mozambique
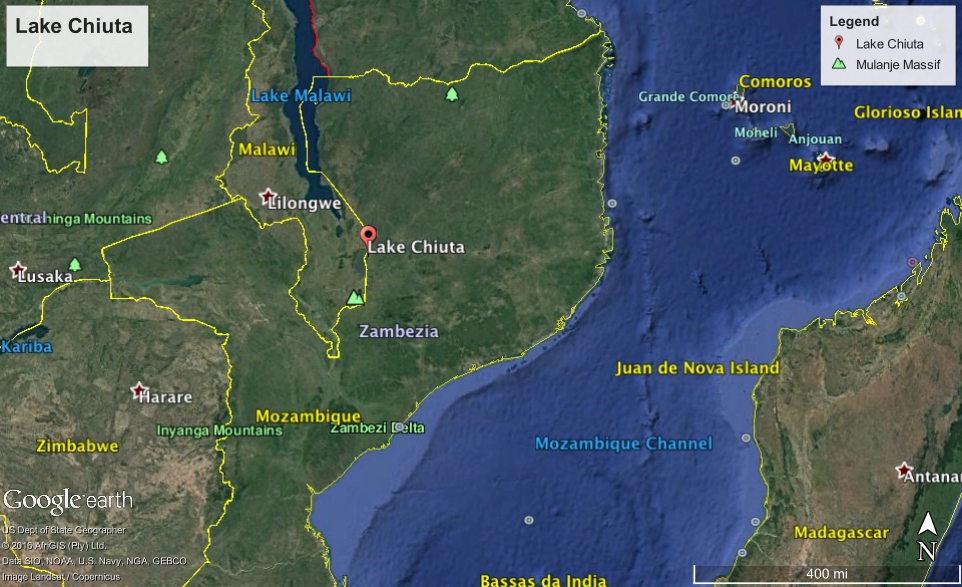 Lake Chiuta
Lake Chiuta

There are only a few species that are commercially viable, chiefly Chambo, Mlamba, and Matemba. US AID reported that hunger in this remote area was leading to the extinction of many species of fish. For more: US AID Report on Lake Chiuta
During a severe El Nino event in 2016, the Lake Chiuta nearly dried up completely.

The World Wildlife Fund seems to blame Malawian fishermen for the problem. Migrants had resorted to unsustainable and destructive fishing practices. But the Nyasa Times says the problem lies with the Mozambique side, with solders allowing them to take excessively. Nyasa Times -- Lake Chiuta
Three Malawian fisherman have been shot, but none have died.

The conflcit is over a specific resource of the lake, not the lake itself.
It should be noted that these are two of the poorest countries in the world. Even by those standards, the area around the lake is quite remote.
Go to Ice Search Engine and Scenario Builder
Link is: https://icedb.shinyapps.io/icedb/
"Water Wars Worry Lake Chiuta Fishers", The Nation
