
| ICE Case Studies
|
|
I.
Case Background |

Eritrea and Djibouti have had a long-standing border dispute. Qatar has tried to act as a mediator in the case. It also stationed its troops on the border to keep the warring parties at bay. They even were able to get four Djibouti troops who had been captured in clashes, released in 2016 after they had been imprisoned during clases in 2008. During the conflict, France gave logistical, medical and intelligence support to Djibouti. The Qatari troop shave been there since June 2010, and for seven years maintained an uneasy peace.
Ras_Doumeira
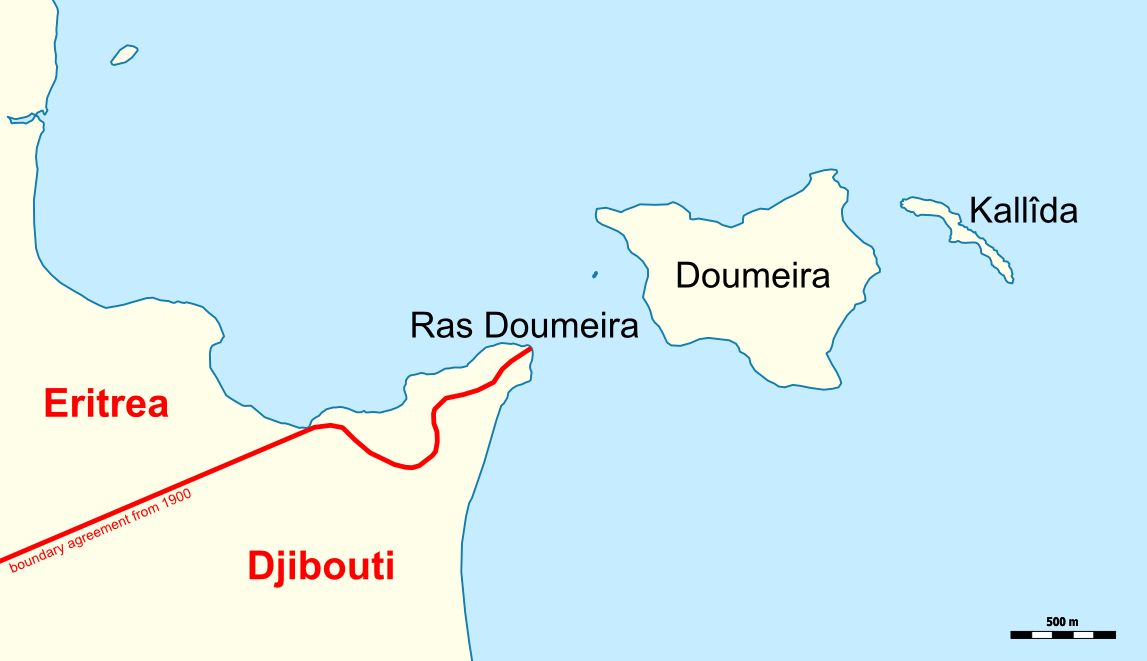
The current diplomatic crisis with Qatar and other Sunni Muslim states made many at home wonder why there were 500 Qatari troops in Africa, out of a total of 12,000 for the entire country. The deployment was also costing the country a lot each year. In the end, the expenditure was useless, as one country cut ties and the other down-graded them.
Djibouti is a small place, but getting more crowded over time. A French colony was established in the 1880s that endured until the 1960s when a plebiscite was held to decide it the citizens wanted to join the new country of Somalia. The vote was no, built primarily on Afar and European residents of the area. It is effectively a city-state, with two-thirds of the population living in Djibouti City. It is however a strategic place with a deepwater port with access to the Red Sea and Indian Oceans.
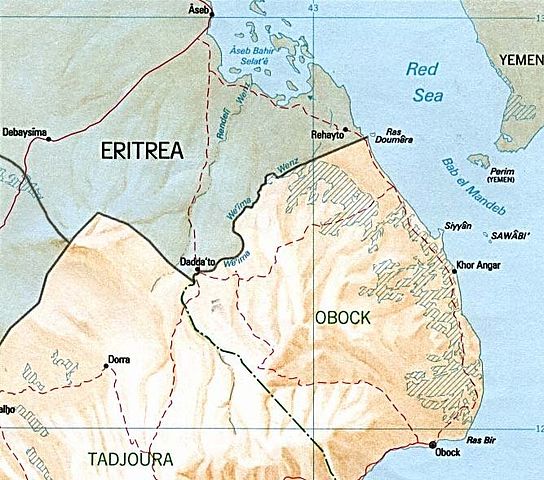
Image from CIA
Djibouti has been home to the large U.S. base at Camp Lemonnier for some time. China has also established both military and economic ties to the region. In April 2015, Saudi Arabia and Djibouti entered into a security cooperation and the UAE is building a base there to eventually train Somali troops.
The conflict started in 2008 when Eritrean troops occupied the disputed area of Ras Doumeira. The border was set by the former colonial powers, Italy and France, following their own, non-violent dispute in 1898. The accommodation was that the area was to be de-militarized.
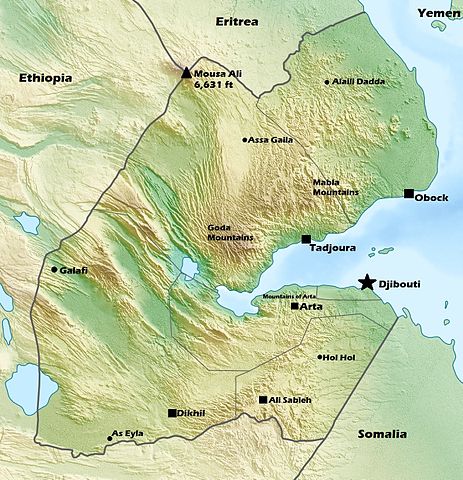
Image from Open Database License (ODbL)
Continent: Africa
Region: East Africa
Country: Djibouti
There are four parts of the small country of Djibouti: The Northern Mountains, Danakil Depression, Grand Bara Desert, and The Southern Mountains.


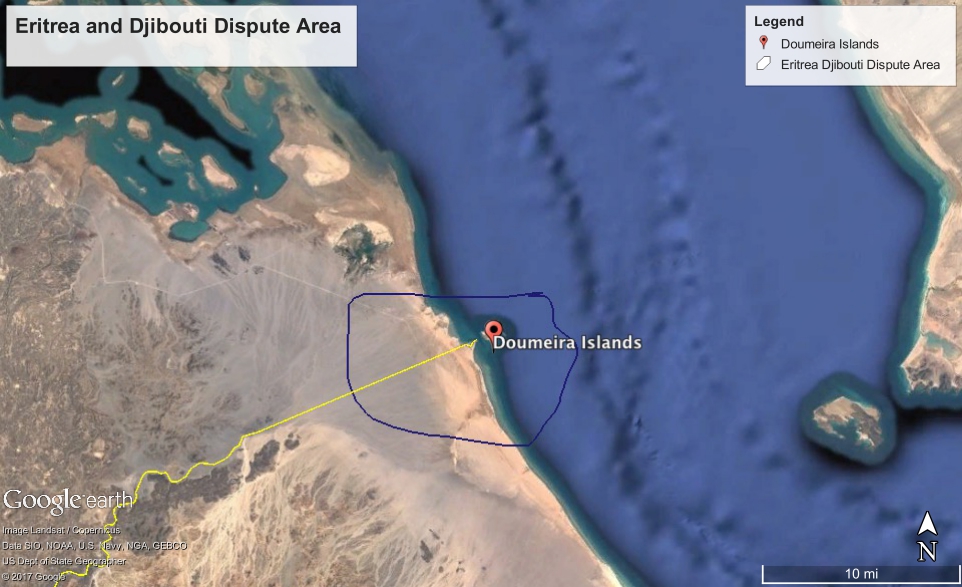
Eritrea has recently added more tension to the case by moving troops into areas of dispute, including the Dumeira Mountain and Dumeira Islands.
Over 40 Djibouti troops were injured as well. Eritrea refused to release fatality numbers, but estimates were that 44 troops from Djibouti died, and 100 from Eritrea.

IV. Environment and Conflict Overlap
Like Eritrea's costly and bloody border dispute with Ethiopia over the desolate Badme Plain, there are few resources at stake in the case, leaving the battle reasons solely towards a symbolic act of controlling these areas solely to embolden the idea of state sovereignty and power in the areas. (See related ICE case.)
The bi-lateral dispute is now one part of a larger regional clash. Eritrea along with several other states, have cut ties to Qatar, joining Yemen, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Egypt, Libra, the Comoros, Bahrain, Senegal, and Yemen. In addition, Chad, Djibouti, Jordan, and Niger, downgraded ties. Thus, both sides in the dispute have now shuttered most relations with Qatar. At the same time, Turkey quickly establishing a security understanding with Qatar and Iran began emergency food shipments.
Immediately after the Qataris abandoned the border, the Eritreans occupied Dumeira Mountain. Djibouti filed a complaint with the African Union. Ehtiopia, a major regional rival of Eritrea, immediately called for AU intervention. Ethiopia has sent troops several times into Somalia to fight Al-Shabab, who have links to the Eritreans.
Go to Ice Search Engine and Scenario Builder
Elias Meseretm "Djibouti says Eritrean soldiers occupy disputed area," Associated Press, June 16, 2017. Go to Article
"Eritrea-Djibouti", International Crisis Behavior, source: https://sites.duke.edu/icbdata/data-collections/ Go to Article
"African Union Urges Restraint in Djibouti-Eritrea Border Spat," Reuyters, June 17, 2017 Go to Article
"Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict", Wikipedia, Accessed June 19, 2017. Go to Article
