
| ICE Case Studies
|
|
I.
Case Background |

After more than 20 years of conflict, and 2.5 million dead, South Sudan voted for, claimed, and became independent in July 2011. One of the reasons for the war was over control of local resources, especially oil. In the end, South Sudan controlled the sources of oil, but Sudan the routes for transportation. The South Sudanese accused the Sudan government of arming various ethnic groups to sow discord, particularly between the Dinka and Nuer. The firing in July 2013 of vice president Riek Machar, a Nuer, by president Salva Kiir, a Dinka. South Sudan is now a desparate place and home to great wood insecurity.
South Sudan was conquered by the Egyptian Sultanate in the 18th century. It later passed to Anglo-Egyptian Sudan and then the country of Sudan upon its independence in 1956. It became the largest in Africa and with a largely Muslim north and a Christian/animist south.
The First South Sudan Civil War started in 1955 and lasted until 1972 and the signing of the Addis Ababa agreement. The deal allows for an autonomous South Sudan region.
The Second South Sudan Civil War lasted from 1983 until 2005 when another agreement was signed. It started when President Nimiery of Sudan imposed Islamic law based on Sahr'ia over all parts of the country. He renounced the Addis Ababa agreement. In 2005 an autonomous government was announced that lasted until the vote for independence that came in 2011. During the Second Civil War, more South Sudanese died at the hands of their countrymen than by Sudanese forces.
More than 98 percent of the population os South Sudan voted for independence so there was great hope for the new nation. Other countries, particularly the United States, also promised financial and development support. Things however quickly turned sour.
In 2012 Sudan attacked a border region and seized it. The region has oil deposits so the marking of the boundary has been a long-contentious item between the two parties. Another agreement set the border and set an understanding on production and transport rules for the oil which needed to pass through Sudan to markets.
President Salva Kiir (a Dinka) and vice-president Riek Machar (a Nuer) have led their tribes in this civil war. It began with an alleged coup attempt by a Nuer faction. Now however, out of 12 million people, 3 million have been forced from their homes. One million have fled the country.
Sudan Map
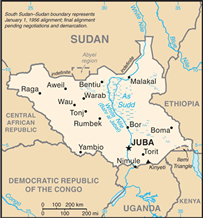
Source: CIA
Conflict began almost from the moment the new country was created.
Continent: Africa
Region: East Africa
Country: South Sudan
South Sudan is not part of the Sahel but rather located in Sub-Saharan Africa. It has been dominated by Nilotic peoples for many centuries.

South Sudan was given a large endowment of oil resources but the conflict has largely scuttled investment and development.
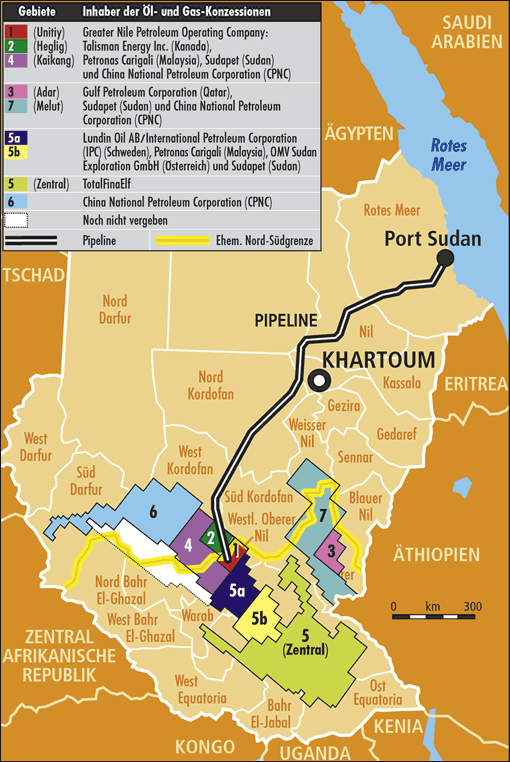
Image thanks to Michael Till-Lambrecht, Wikipedia Commons
Source: US AID, 2001
Clement Sefa-Nyarko argues that it is necessary for analysts to put oil in context. It is a reason to fight, but the inter-tribal warfare in South Sudan goes back to 1955 when revolt against the Anglo-Egyptian rule broke out. It took nearly 20 years before there was a coalescence of efforts under a united umbrella.
Ethnic Groups in South Sudan (Zoom in to see detail)
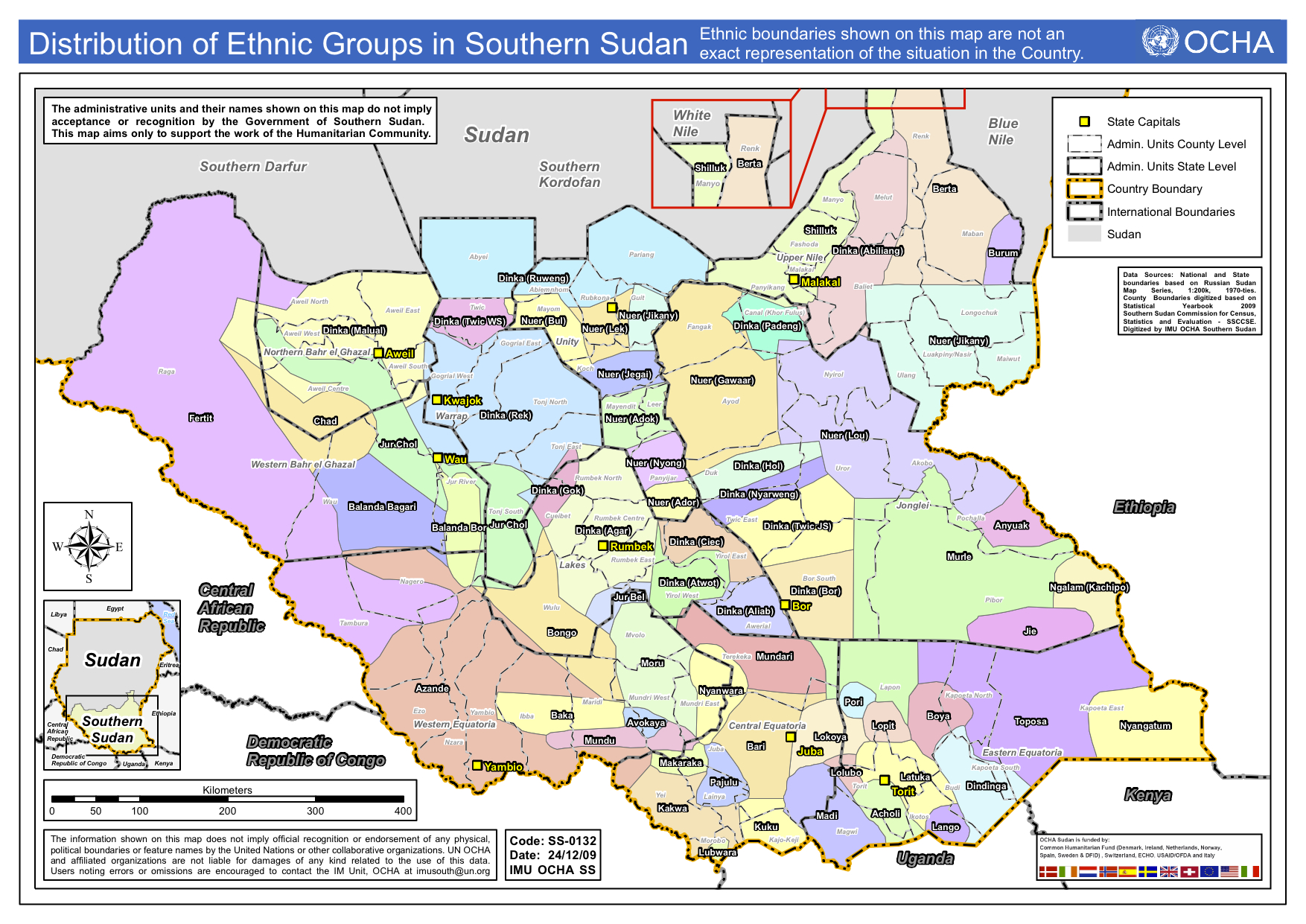
Source: UN OCHA
The south of the country is in a tropical zone, but it in the north it is a more transitional and dry as it turns into the Sahel.

While the civil war is nominally a conflcit between Dinka and Nuer, there may be as many as nine differing groups in conflict.
In addition to the many who died in the pre-independence civil wars (2.5 million), a further 300,000 have died in civil war since independence. Three million are now displaced.
300,000 have died in civil war since independence.

Oil is certainly a factor in the conflict but ethnic rivalry has made this conflict particularly vicious.
Obviously Sudan has a role in the conflict, as well as Ethiopia. There are actually many tribal groups in conflict in in the country. The Lord's Army also operates in the south of the country.
Go to Ice Search Engine and Scenario Builder
ICE Cases Related to South Sudan and Sudan
See Jonglei ICE Case
SeeSudan Resources or Religion ICE Case
South Sudan: A Civil War by Any Other NameInternational Crisis Group, April 2014
https://www.crisisgroup.org/africa/horn-africa/south-sudan/south-sudan-civil-war-any-other-name
Clement Sefa-Nyarko, "Civil War in South Sudan: Is It a Reflection of Historical Secessionist and Natural Resource Wars in “Greater Sudan”?, African Security, Volume 9, Issue 3, June 2016.
"The Root Cause of the Darfur Conflict: A Struggle Over Controlling an Environment that Can No Longer
Support all the People Who Must Live on It", The Sudan Watch July 2006.
http://sudanwatch.blogspot.com/
